Properties:
PESA is a multivariate scale and corrosion inhibitor with non-phosphor and non-nitrogen, it has good scale inhibition and dispersion for calcium carbonate, calcium sulfate, calcium fluoride and silica scale, with effects better than that of ordinary organophosphines. When built with organophosphates, the synergism effects are obvious.
PESA has good biodegradation properties, it can be widely used in circulating cool water system in situation of high alkaline, high hardness and high pH value. PESA has good synergism with chlorine and other Water Treatment Chemicals.
CAS No. : 51274-37-4;109578-44-1
Molecular Formula: HO(C4H2O5M2)nH Molecular weight: 400-1500
Structural Formula:
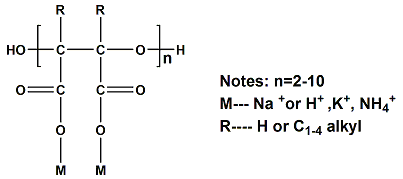
Specification:
| Items | Index | |
|---|---|---|
| Appearance | Colorless or amber transparent liquid | White powder |
| Solid content, % | 40.0 min | 90.0min |
| Density (20℃), g/cm3 | 1.30 min | – |
| pH(1% water solution) | 10.0-12.0 | 10.0-12.0 |
Usage:
PESA can be used in system of oilfield refill water, crude oil dehydration and boiler;PESA can be used in circulating cool water system of steel, petrochemical, power plant, medicine.
Package and Storage:
PESA liquid: 200L plastic drum,IBC(1000L),customers’ requirement.
PESA solid: 20kg/bag,customers’ requirement.
Storage for ten months in shady room and dry place.
Safety Protection:
Alkaline, Avoid contact with eye and skin, once contacted, flush with water.
PESA protective measures:
PESA stands for Protected Extensible Security Architecture, which is a security framework for network devices developed by Cisco Systems.
The PESA framework includes a range of protective measures such as:
- Secure Boot: Ensuring that the firmware and software running on network devices are genuine and unmodified.
- Hardware Tamper Detection: Detecting any attempt to physically tamper with network devices.
- Secure Management: Enabling secure remote management of network devices with strong authentication and encryption.
- Traffic Encryption: Encrypting network traffic to protect against eavesdropping and interception.
- Access Control: Controlling access to network resources based on user identities, roles, and policies.
- Intrusion Prevention: Detecting and blocking attempts to exploit known vulnerabilities or launch attacks.
- Network Segmentation: Separating different parts of the network to reduce the impact of a security breach.
- Redundancy and Resilience: Providing backup and failover mechanisms to ensure continuous operation in case of a failure or attack.
These measures help to protect network devices and prevent unauthorized access, data theft, and other security threats.
