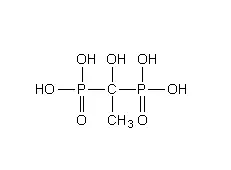
HEDP is the abbreviation of 1-Hydroxy Ethylidene-1,1-Diphosphonic Acid. It is a commonly used water treatment agent, often used as scale and corrosion inhibitor in the field of water treatment, the molecular weight structural formula can be seen in the following chart, the product is widely used in industrial circulating cooling water system, printing and dyeing industry, electroplating industry and many other fields.
| CAS No. | 2809-21-4 | EINECS No. | 220-552-8 |
| Molecular Formula | C2H8O7P2 | hedp molecular weight | 206.02 |
hedp chemical structure
Effects of HEDP on water quality
Scale inhibition
HEDP can form stable complexes with calcium, magnesium and other metal ions in water. For example, calcium and magnesium ions in water are easily combined with carbonate and other anions to form calcium carbonate, magnesium carbonate and other scale. The phosphonic acid group in HEDP can chelate with calcium and magnesium ions. It is like a “cage” wrapping up calcium and magnesium ions, preventing them from precipitating with carbonate and other anions, thus preventing the formation of scale. This complexation can effectively reduce the activity of calcium and magnesium ions in water, and reduce the deposition of scale on the surface of equipment (such as heat exchangers, pipe walls, etc.). – In industrial cooling water, if scale is deposited in large quantities, the heat exchange efficiency will be reduced. After using HEDP, due to the inhibition of scale generation, it can make the equipment maintain good heat conduction performance and improve the operating efficiency of the equipment.
Corrosion inhibition
HEDP is able to form a protective film on metal surfaces. Taking the surface of steel as an example, the phosphonic acid group in the HEDP molecule can be adsorbed on the surface of steel and form a dense protective film through chemical adsorption or physical adsorption. This film can prevent corrosive substances such as dissolved oxygen and chloride ions in water from coming into direct contact with the metal. Dissolved oxygen in water is an important factor causing metal corrosion, it will occur on the metal surface electrochemical corrosion reaction. The protective film formed by HEDP can effectively block the contact between oxygen and metal, thus slowing down the corrosion rate of metal and extending the service life of the equipment.
Effects on microorganisms
HEDP itself does not have strong bactericidal and algaecidal properties, but because it inhibits the formation of scale and fouling, it indirectly reduces the attachment substrate needed for microbial growth. Microorganisms (e.g., bacteria, algae, etc.) often need to attach to solid surfaces in water in order to grow and reproduce better. When HEDP prevents the formation of scale, it makes it difficult for microorganisms to find suitable attachment points, thus inhibiting microbial growth to a certain extent. However, if the microbial content in the water is originally high, HEDP alone may not be able to effectively control the microbial community, but also need to be used in conjunction with the use of other water treatment chemicals such as biocides.
